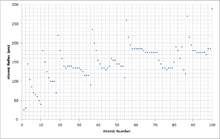
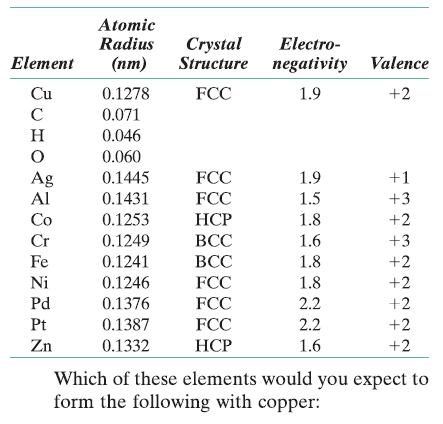
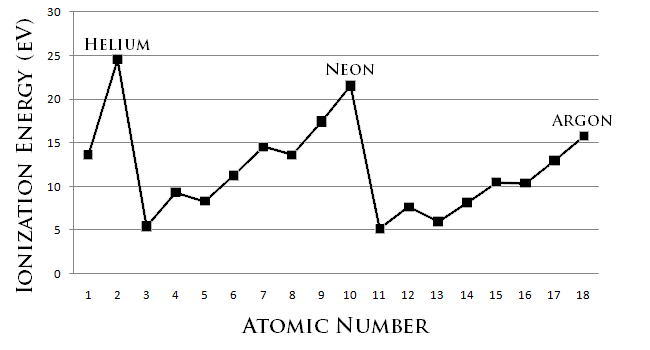
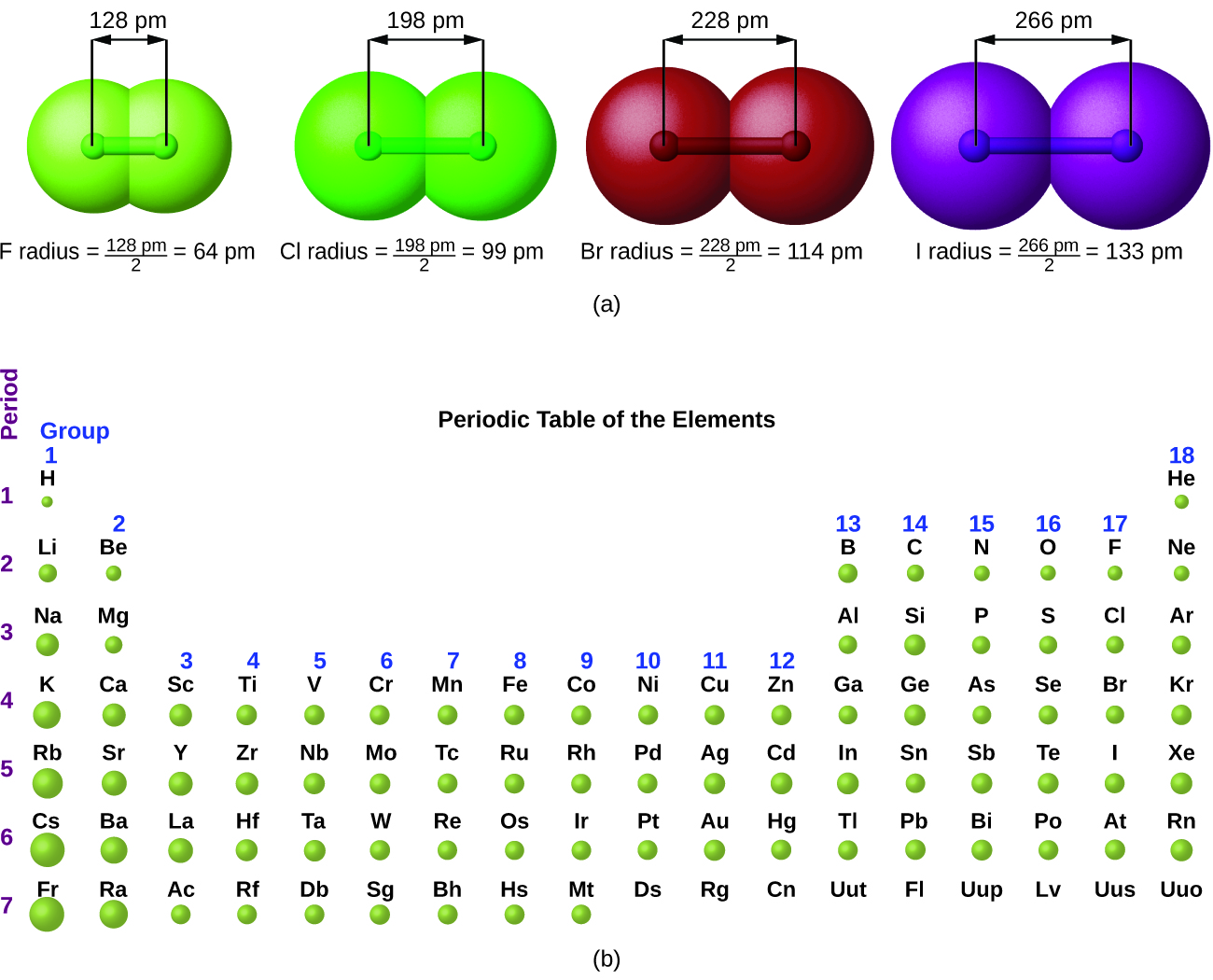
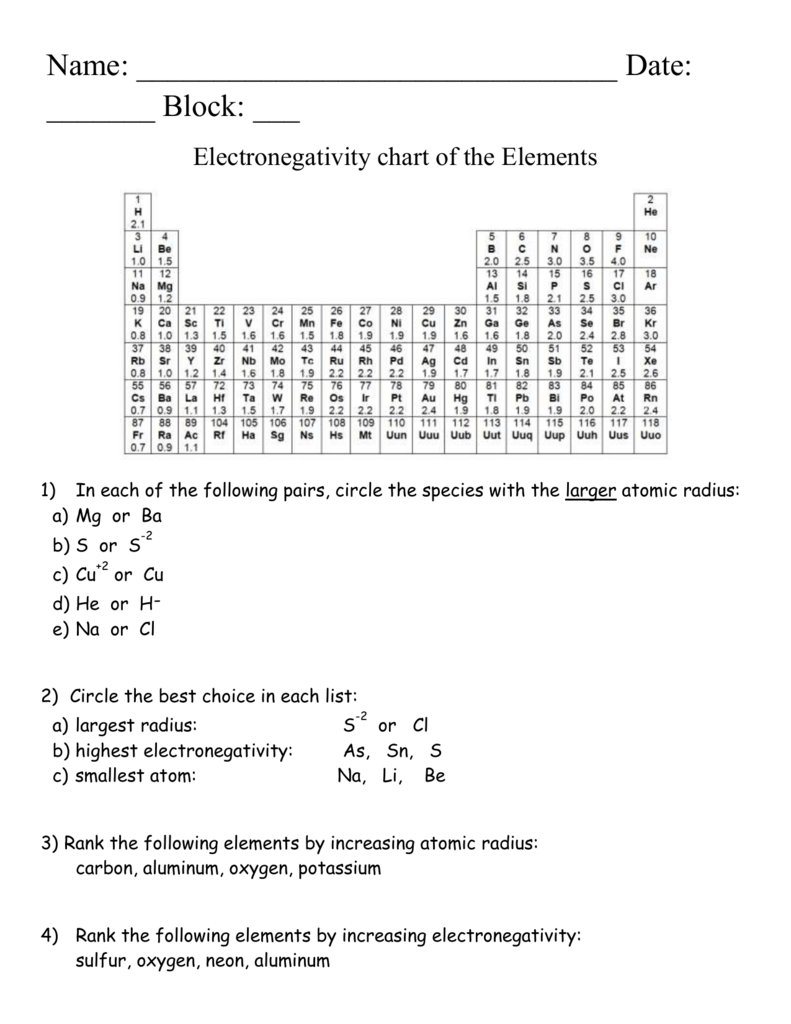
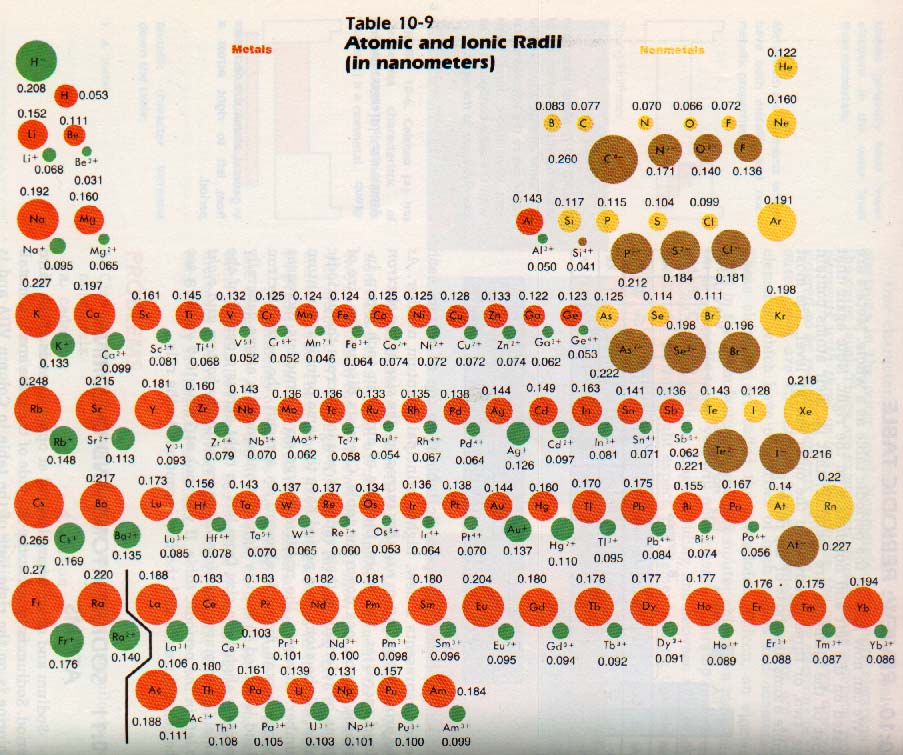
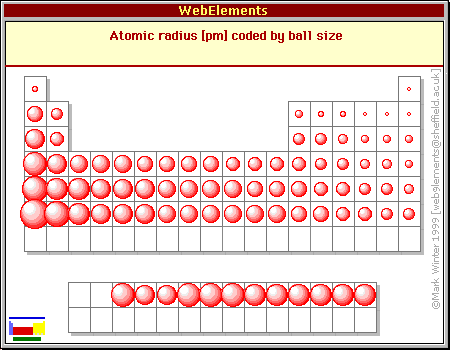
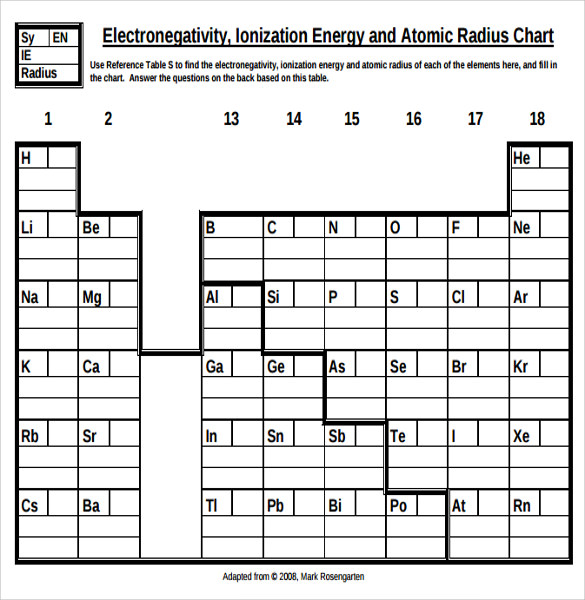
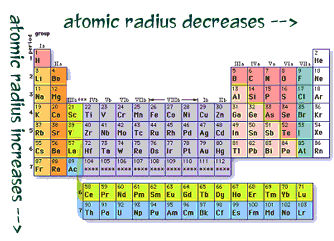
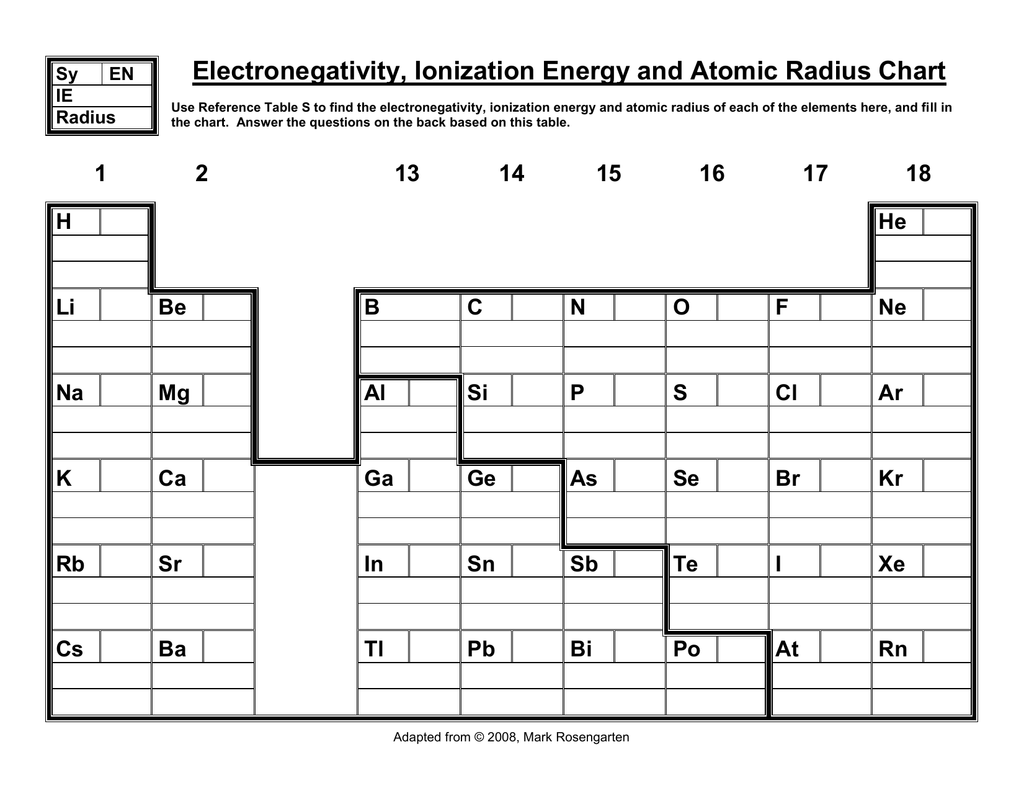
Atom Radius Chart
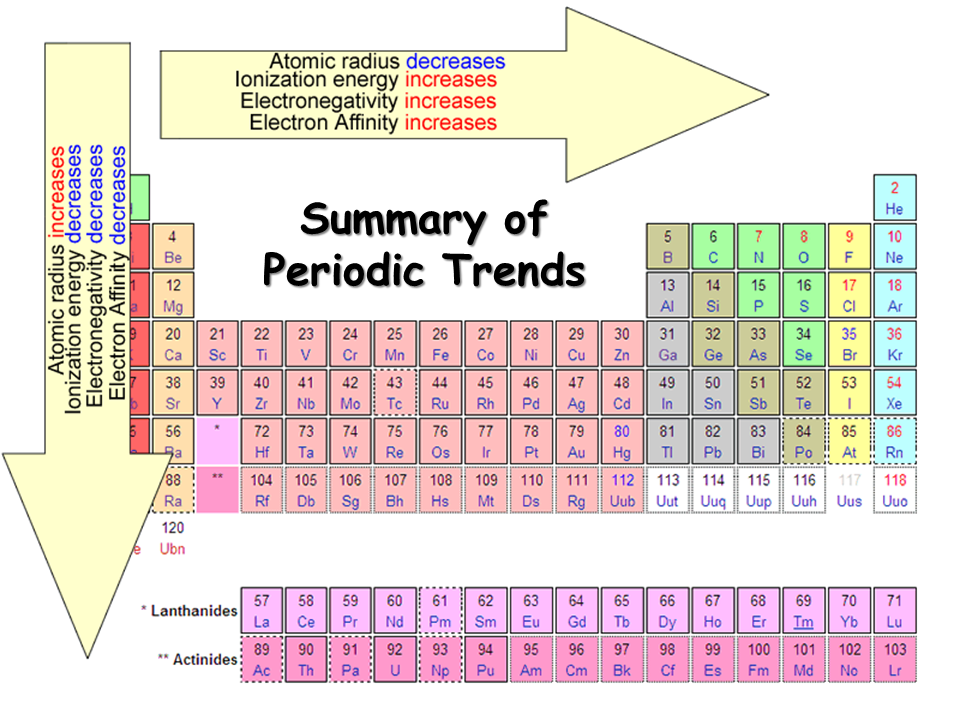
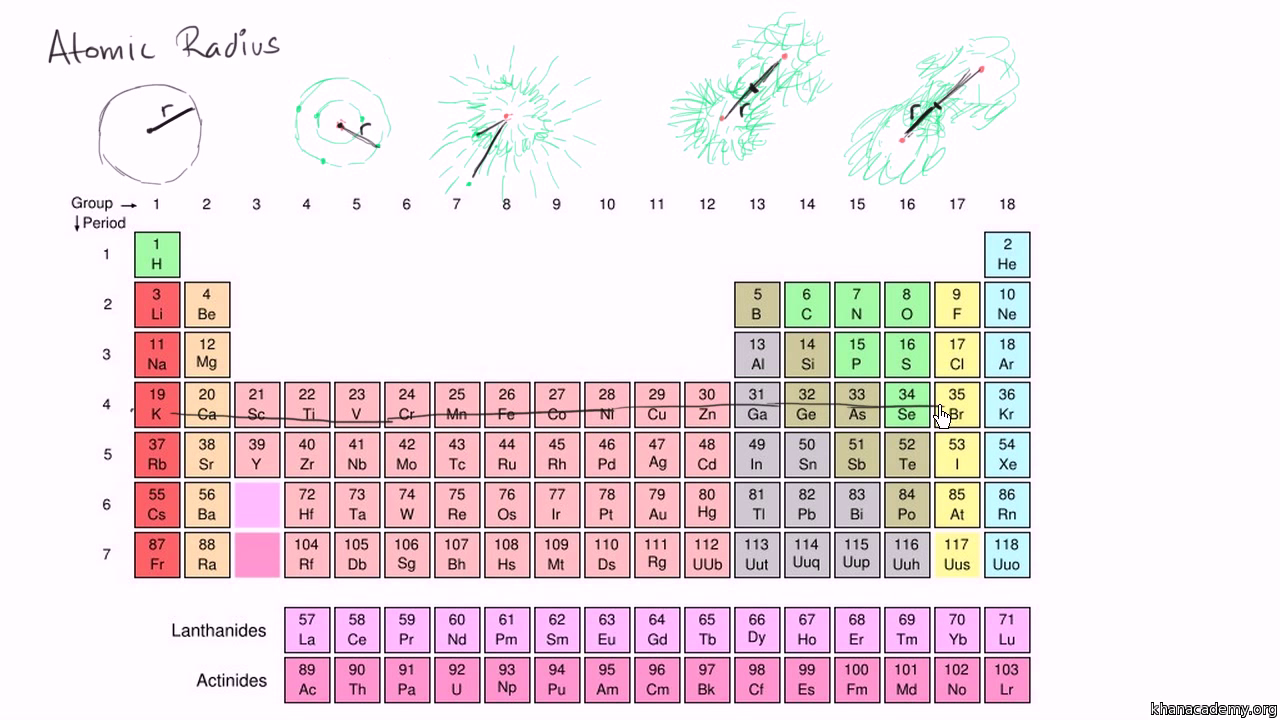
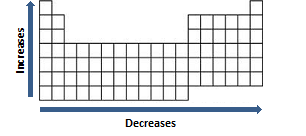
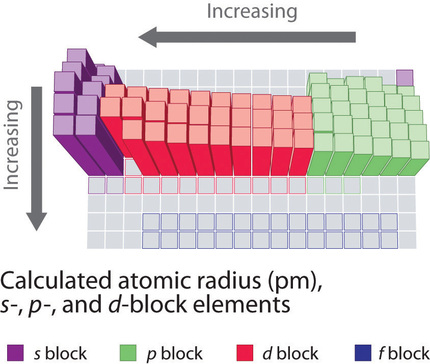
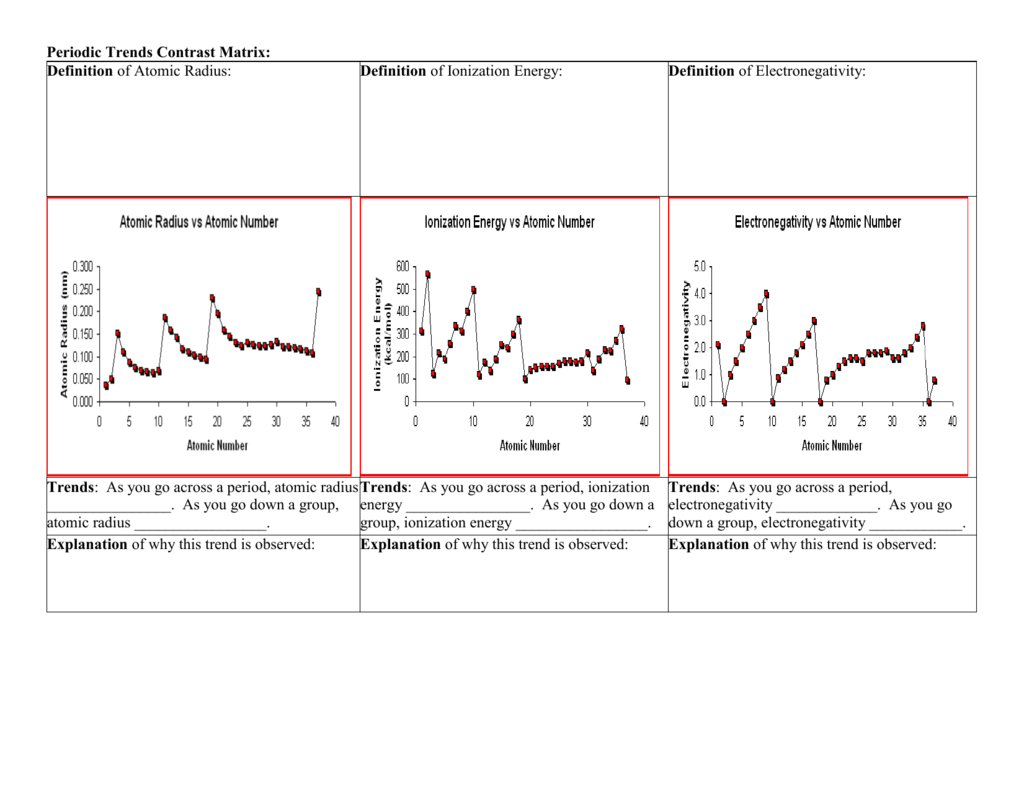
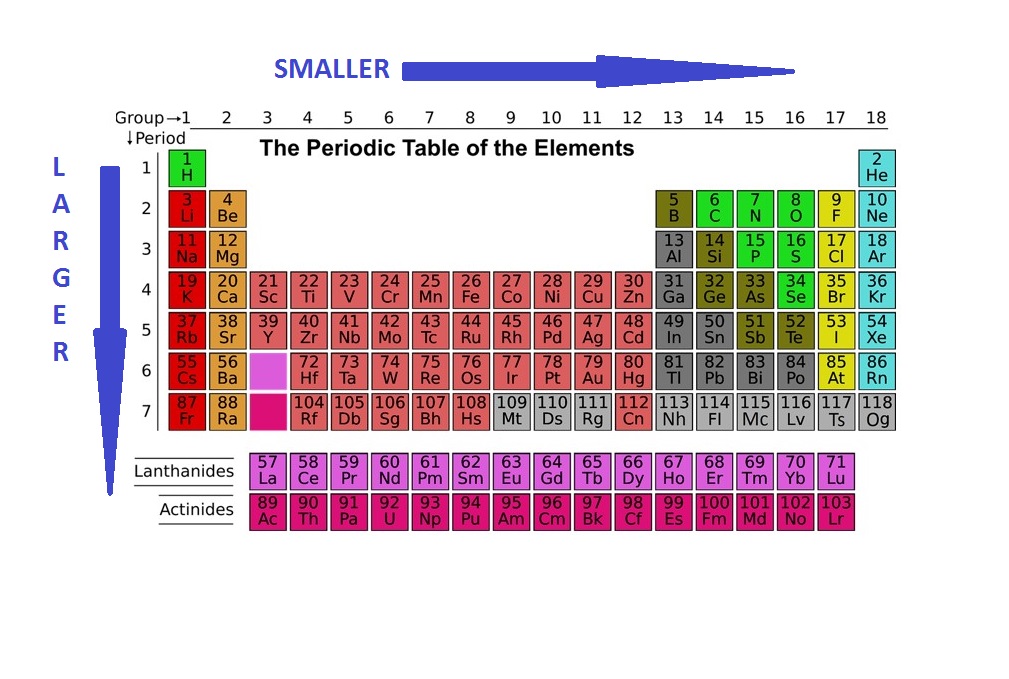
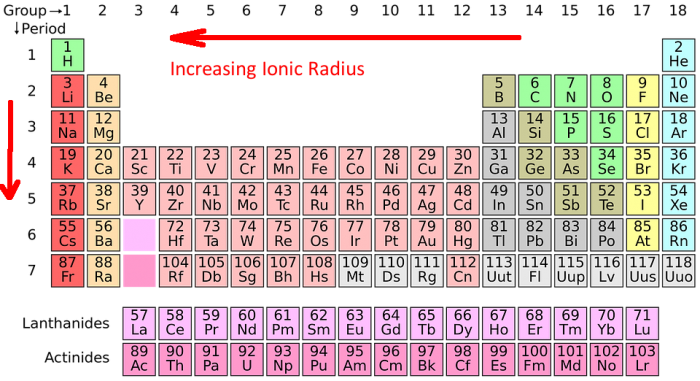
Periodic table of elements with atomic radius trends in the below periodic table you can see the trend of atomic radius.
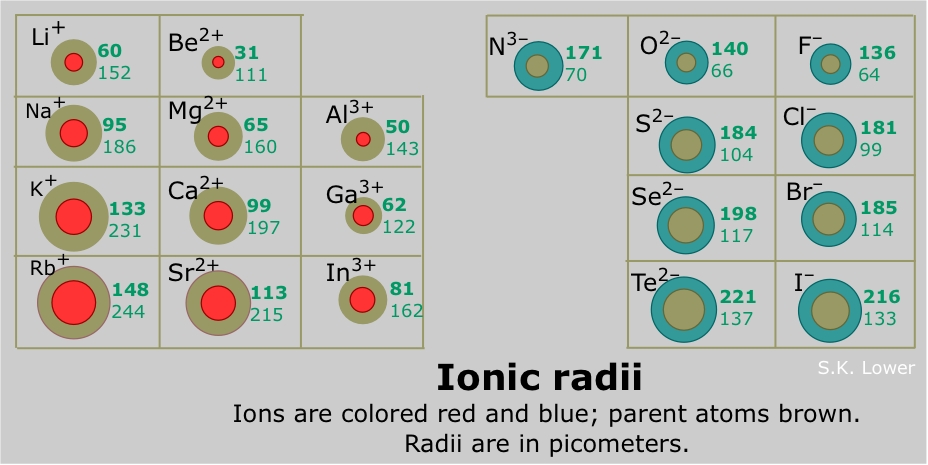
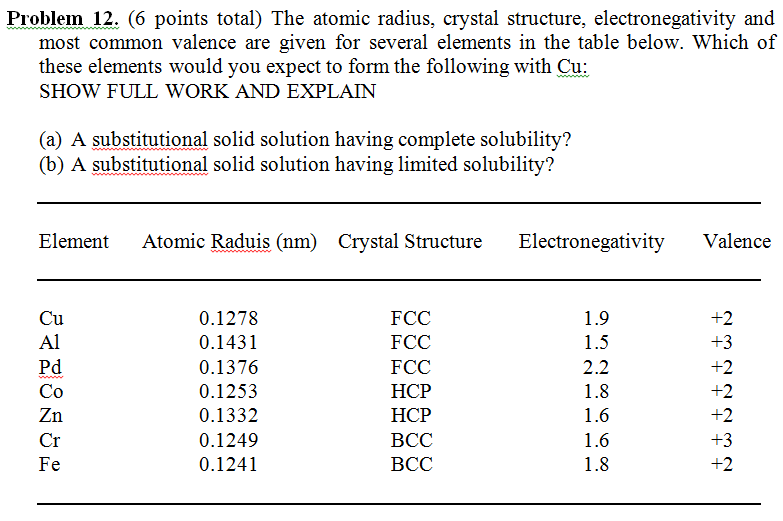
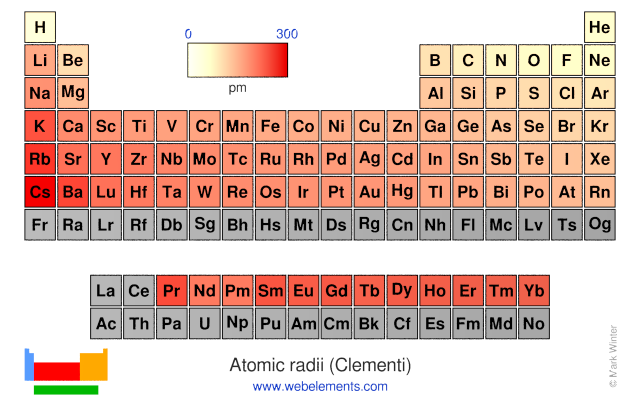
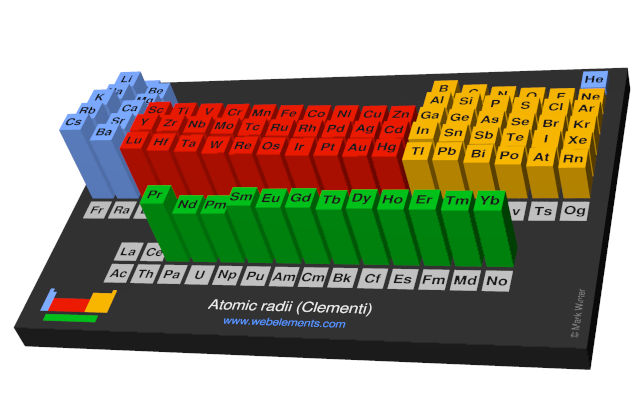
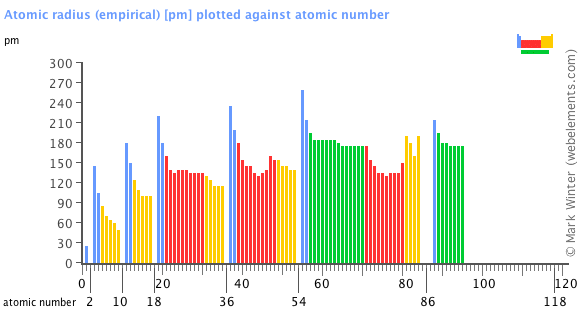
Atom radius chart. Atomic radius trend on the periodic table the size of neutral atoms is drawn from the atomic radius which is half the distance between two atoms that are just touching each other. If the two atoms are of the same kind then the covalent radius is simply one half of the bond length. Atomic radius is one of the periodic properties of the elements.
This atomic radius chart table gives the atomic radius of all the elements of periodic table in pm. Common properties abundance in earth s crust. If you look at the table you can see there is a clear trend in atomic radius.
Over 3 600 nuclides isotopes. The van der waals radius r w of an atom is the radius of an imaginary hard sphere representing the distance of closest approach for another atom. Atomic radii have been measured for elements.
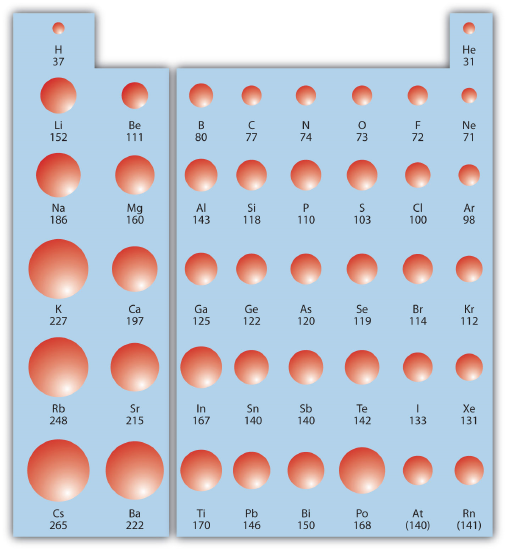
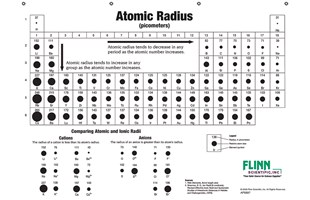
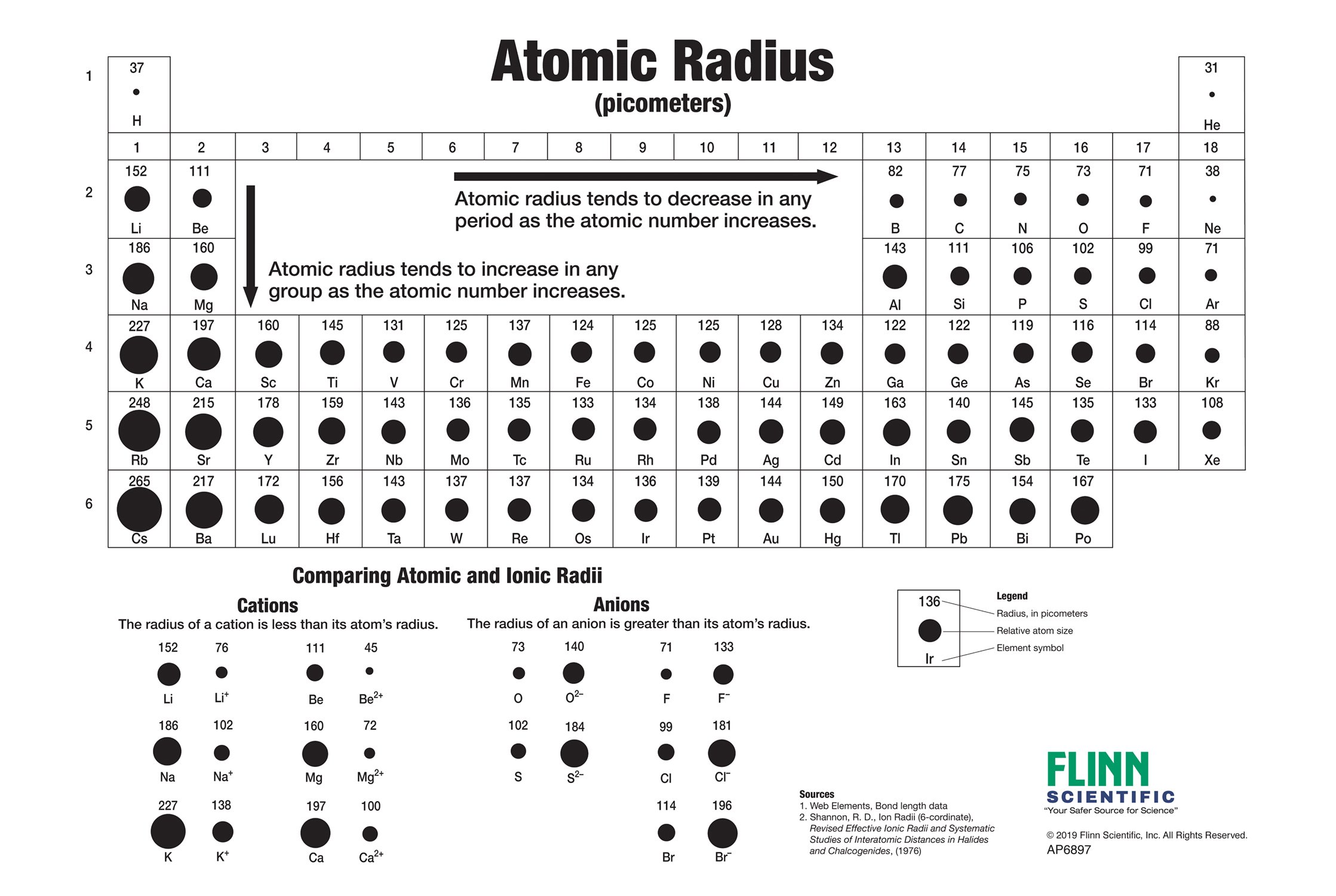
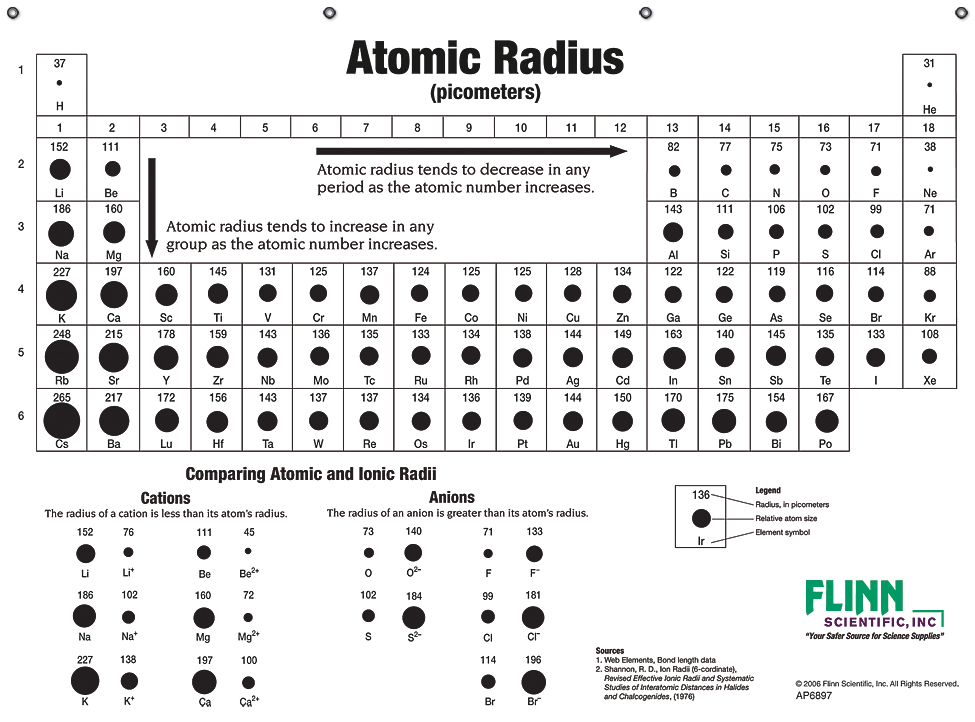
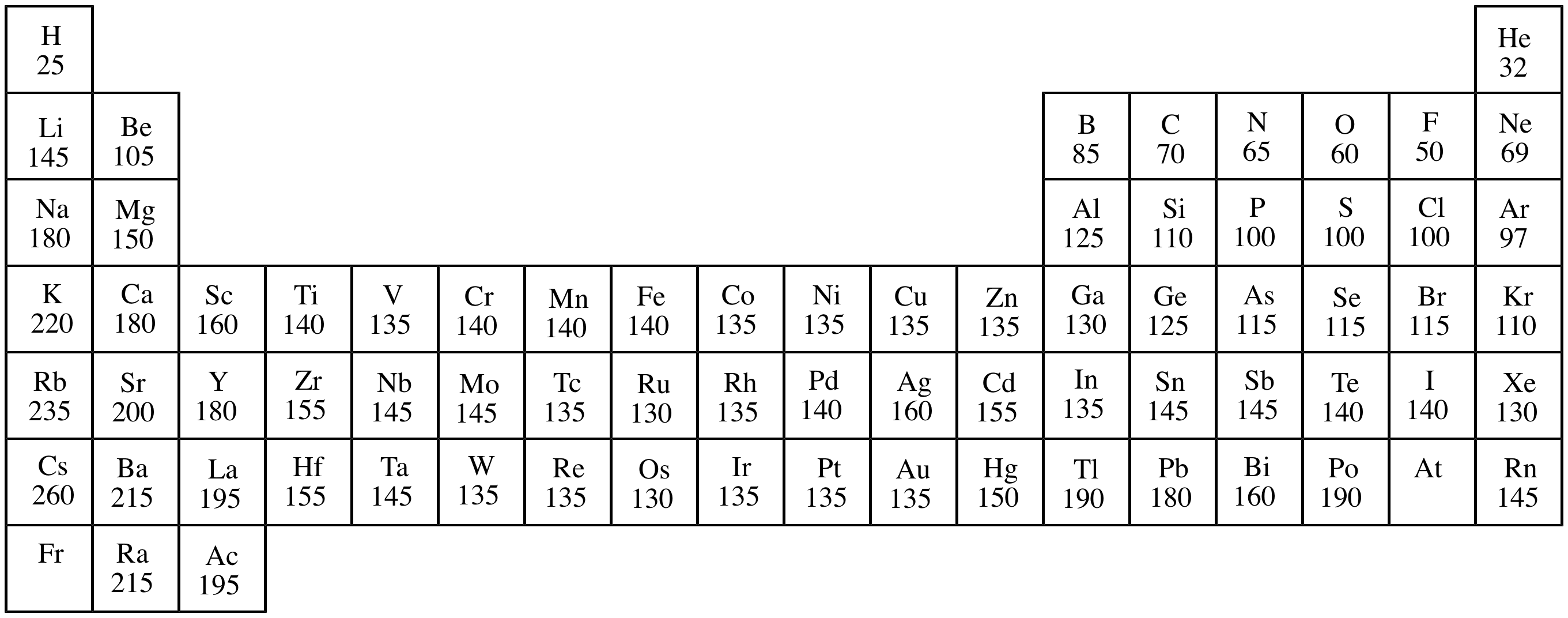
The element names in 10 different languages. In addition chemistry and technical terms are linked to their definitions in the site s chemistry and environmental dictionary. The periodic table of the elements including atomic radius 1 18 hydrogen 1 h 1 01 31 2 alkali metals alkaline earth metals transition metals lanthanides actinides other metals metalloids semi metal atomic radius nonmetals 6 94 halogens noble gases element name 80 symbol beryllium picometers mercury hg 200 59 132 atomic lithium avg.
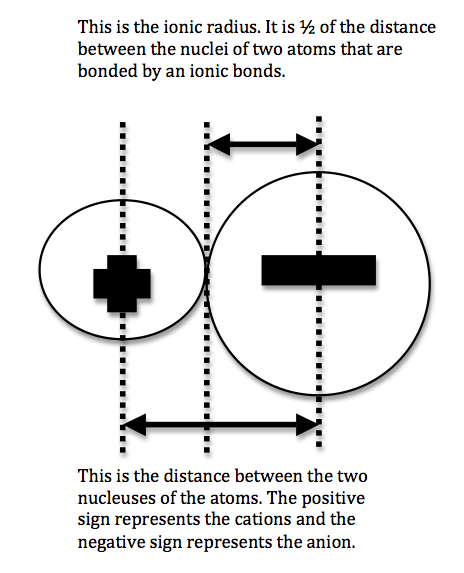
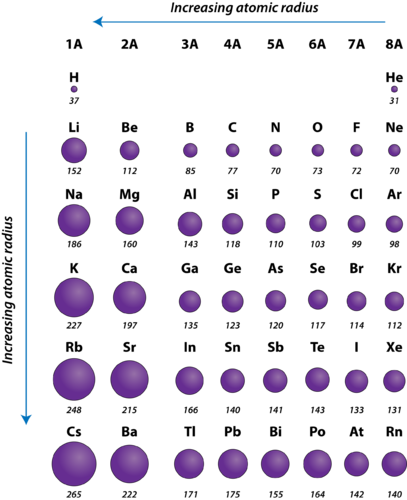
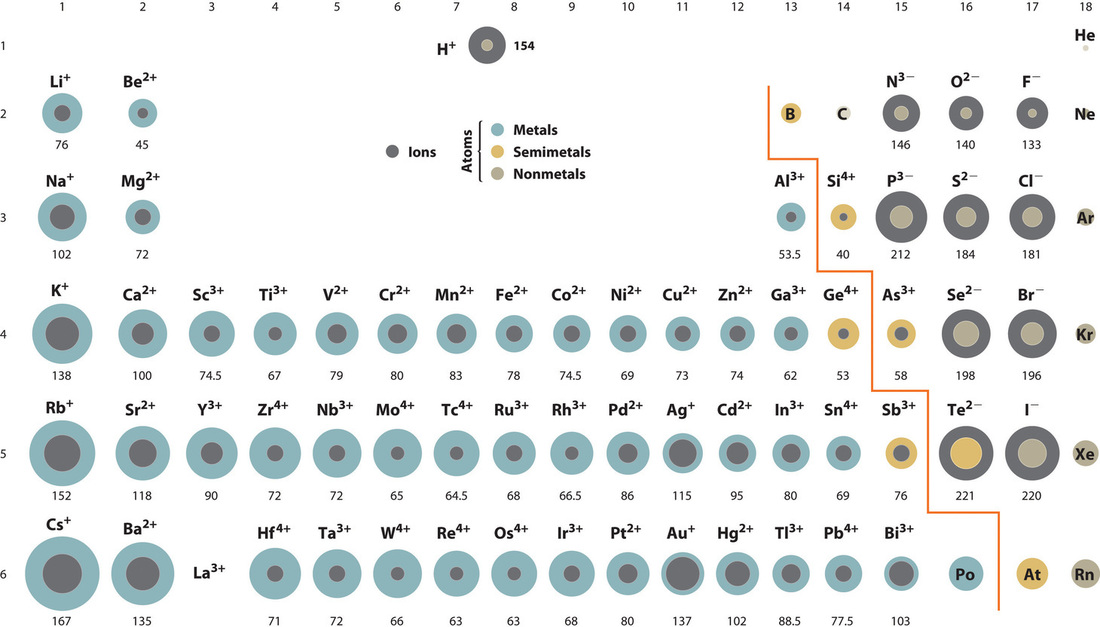
The atomic radius is defined as one half the distance between the nuclei of identical atoms that are bonded together. Since the boundary is not a well defined physical entity there are various non equivalent definitions of atomic radius. For uranium atom the van der waals radius is about 186 pm 1 86 10 10 m.
Click here to buy a book photographic periodic table poster card deck or 3d print based on the images you see here. Who when where. Up to 40 properties chemical physical.
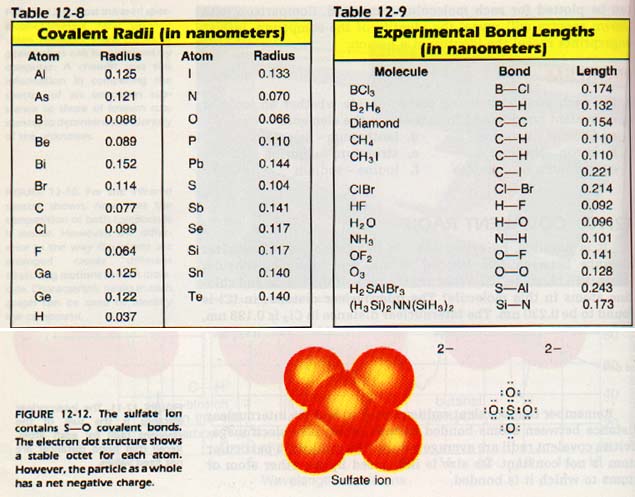
Assuming spherical shape the uranium atom have volume of about 26 9 10 30 m 3. Over 4 400 nuclide decay modes. The covalent radius of an atom can be determined by measuring bond lengths between pairs of covalently bonded atoms.
Click on element atomic number element symbol element name and element atomic radius headers to sort. The atomic radius of a chemical element is the distance from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost shell of the electron.






/PeriodicTable_AtomSizes-56a131193df78cf772684720.png)



/chart-of-periodic-table-trends-608792-v1-6ee35b80170349e8ab67865a2fdfaceb.png)

/chart-of-periodic-table-trends-608792-v1-6ee35b80170349e8ab67865a2fdfaceb.png)