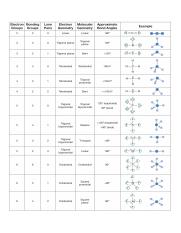
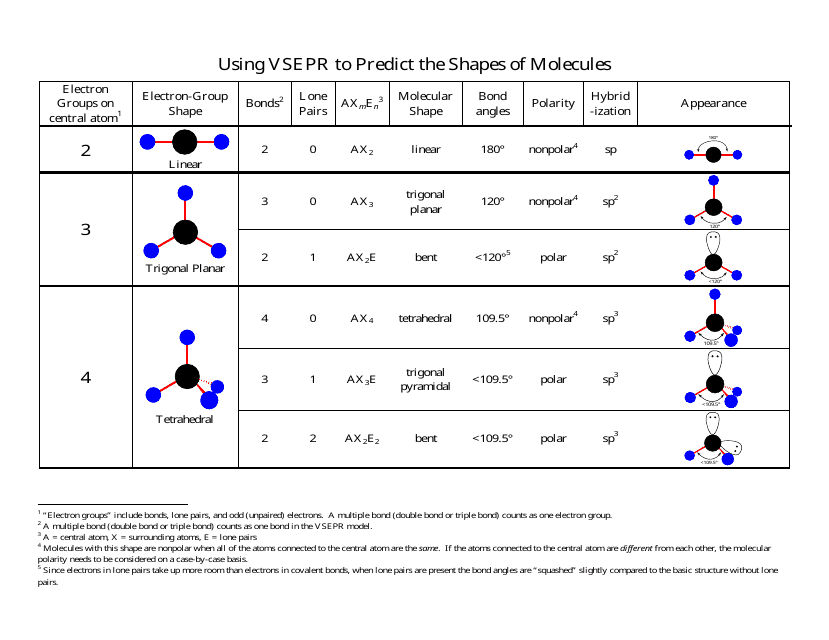
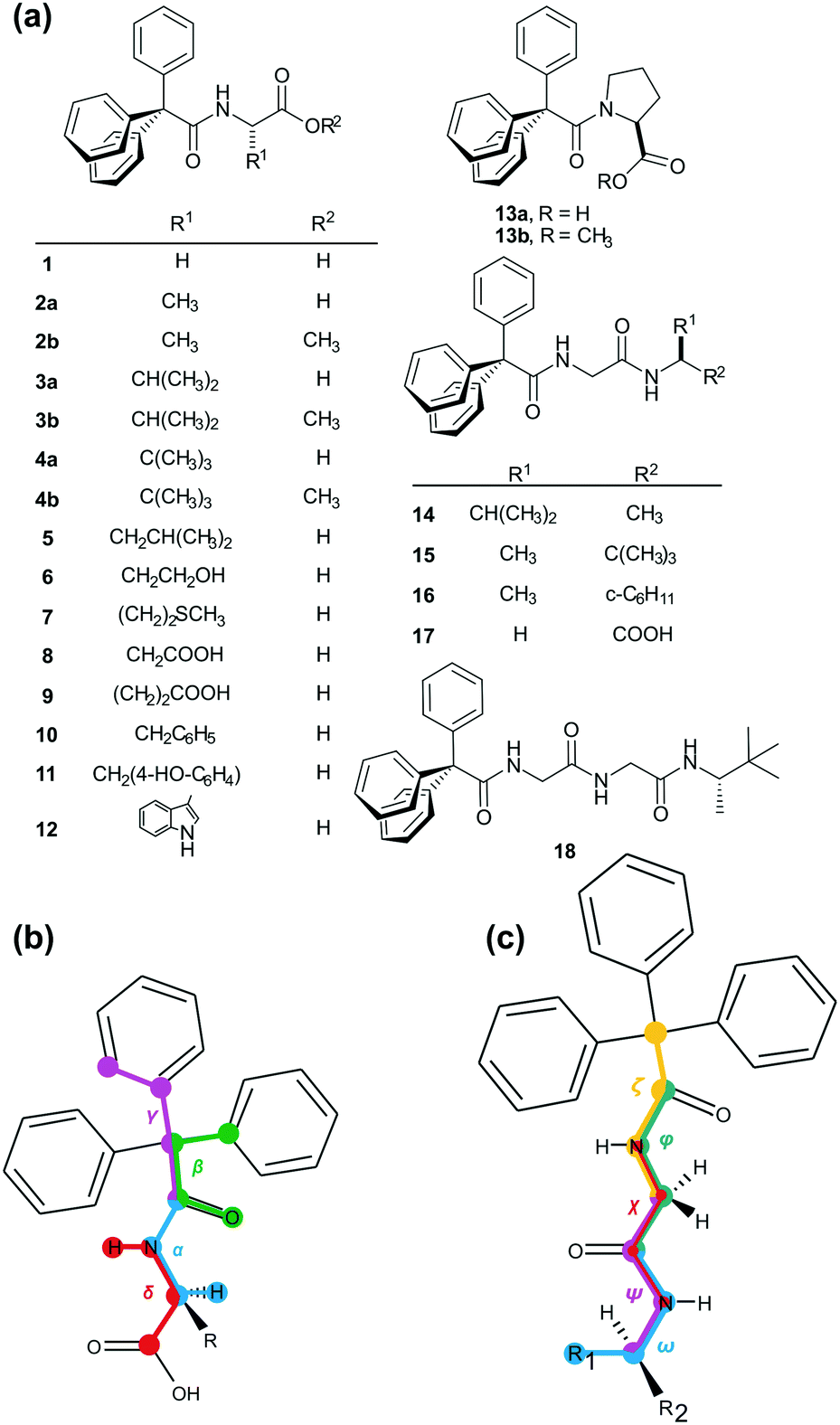
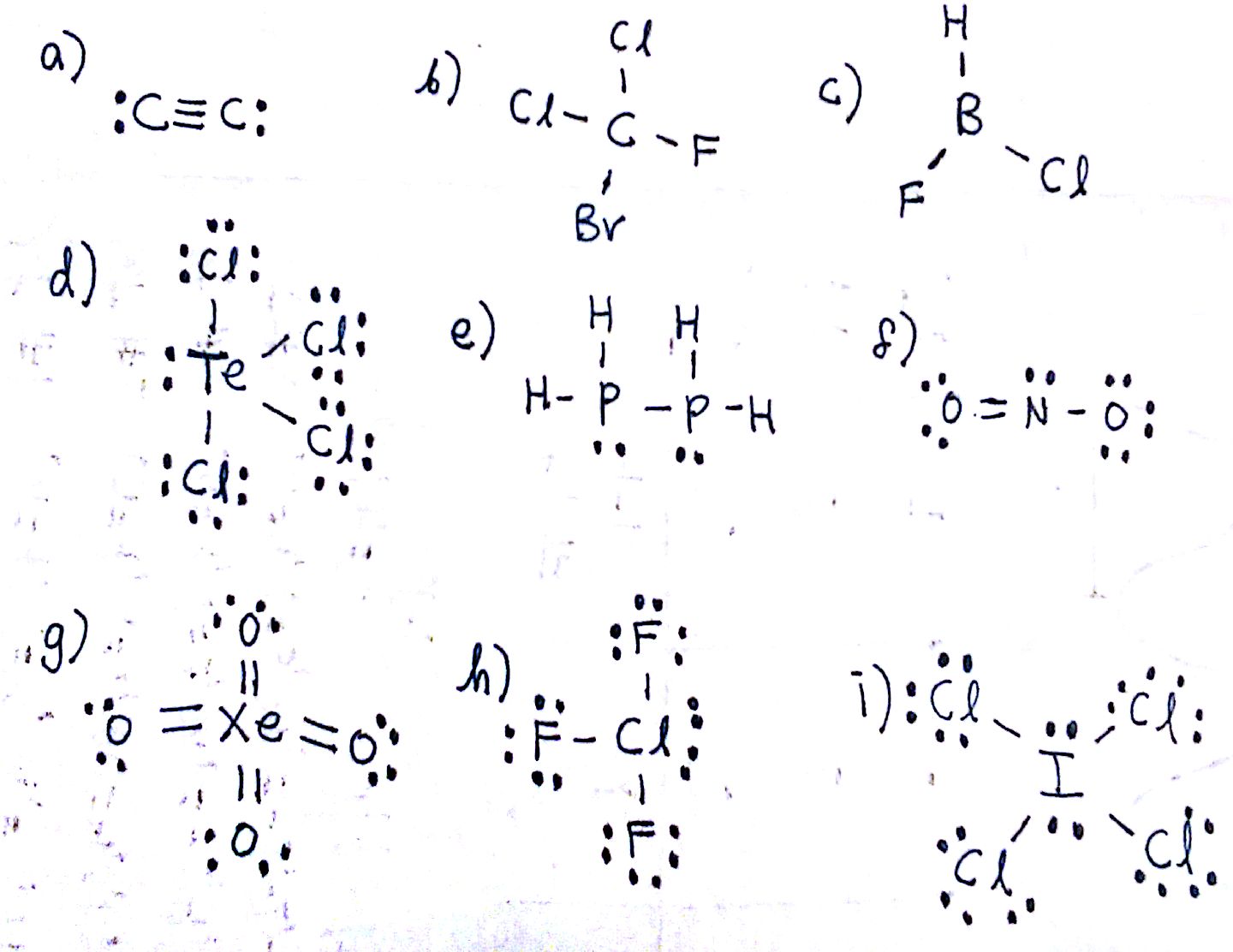Molecular Bond Angles Chart
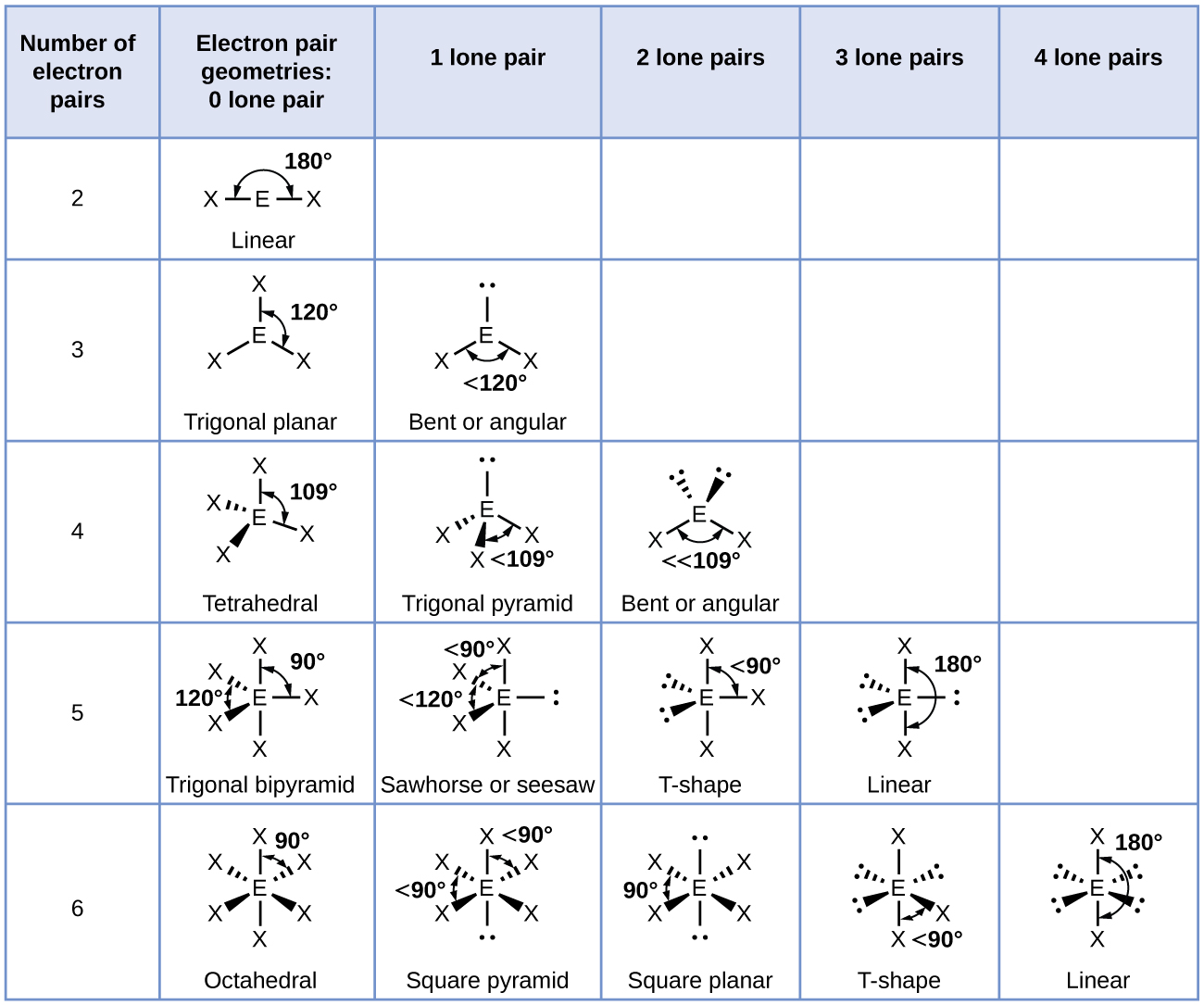
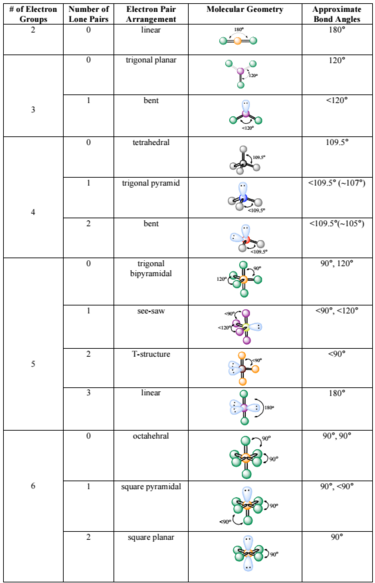
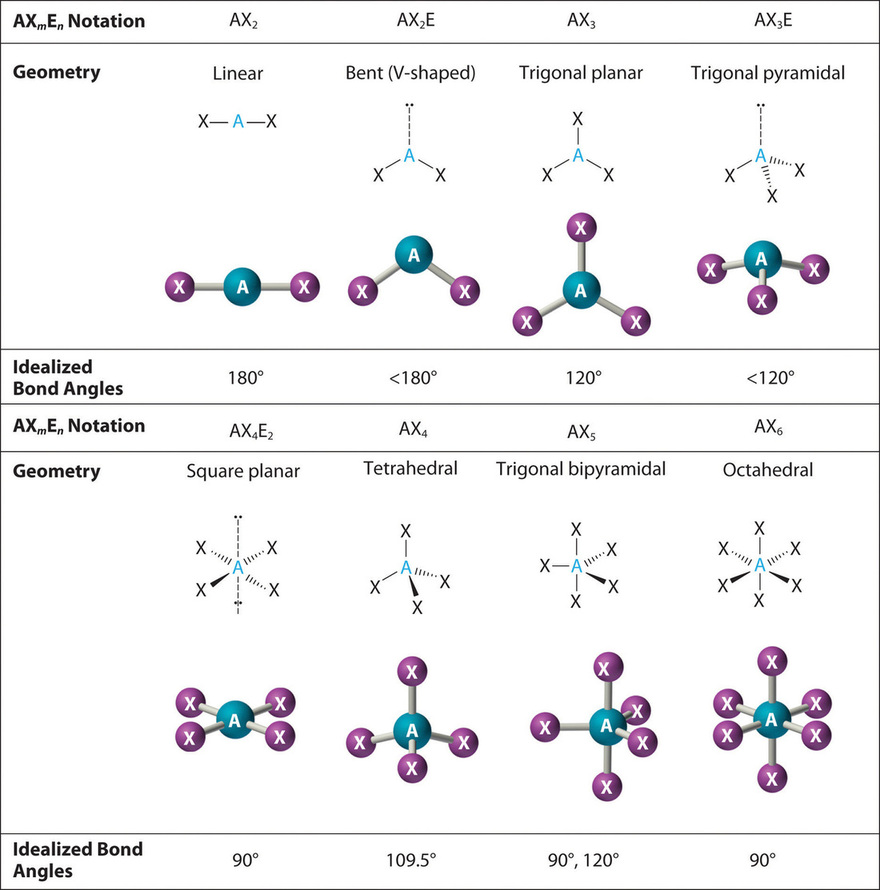
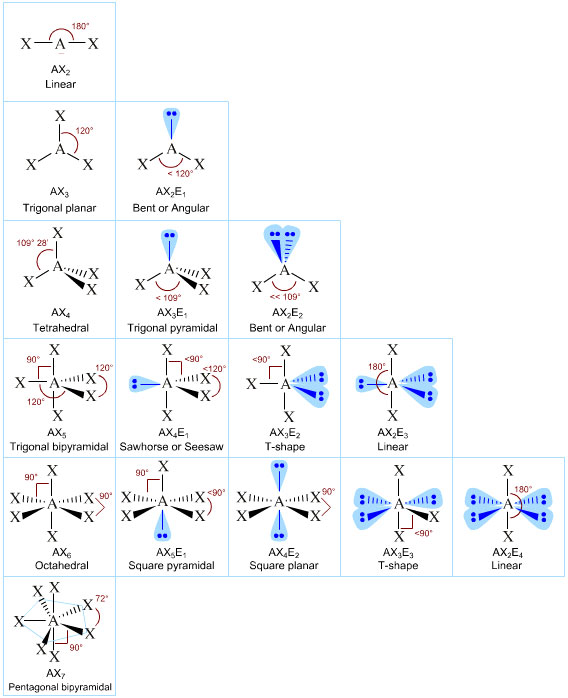
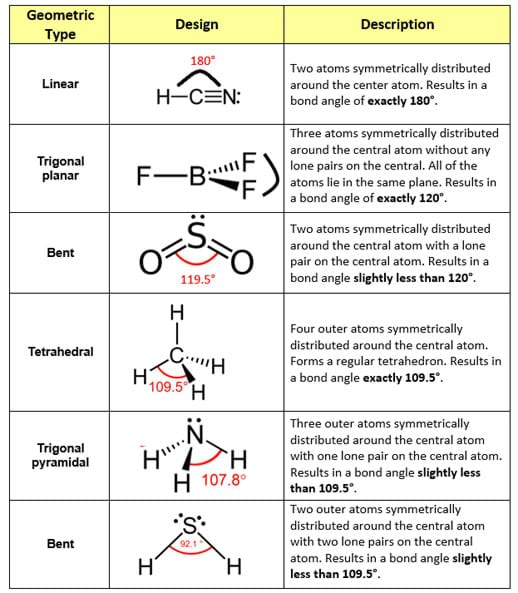
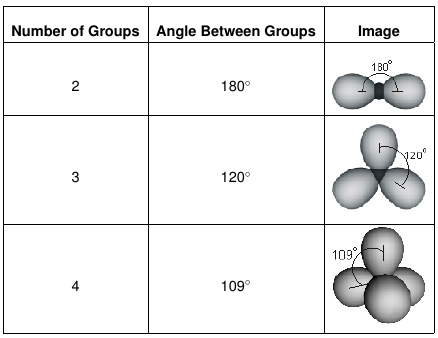
In the linear configuration bond angle 180º the bond dipoles cancel and the molecular dipole is zero.
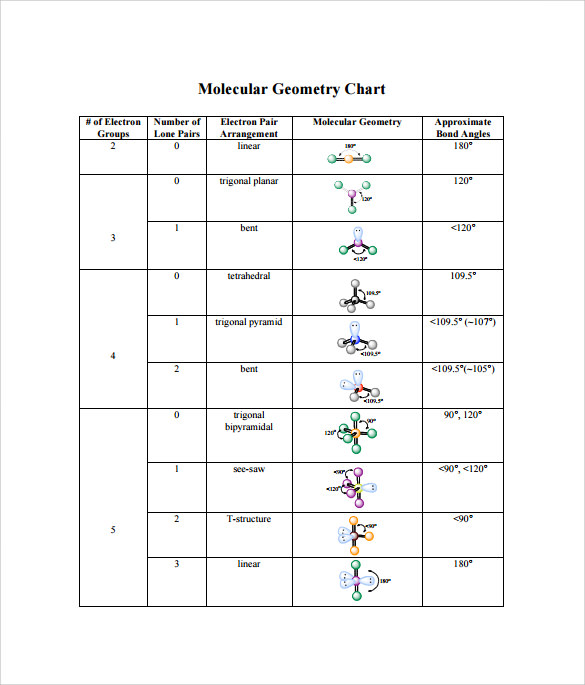
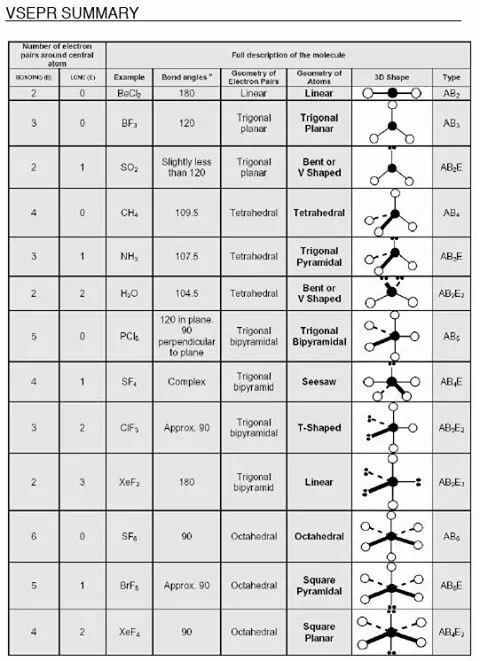
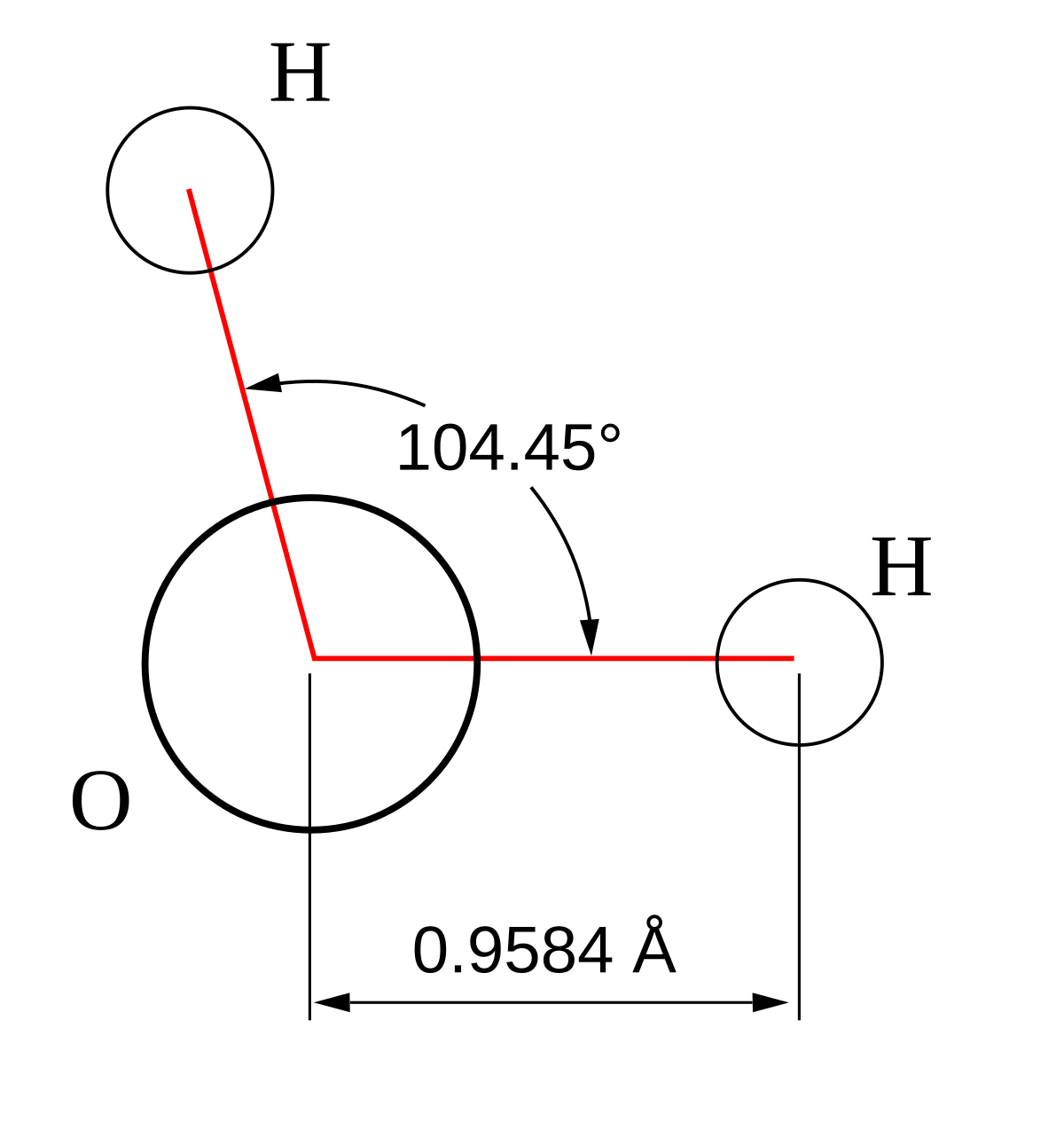
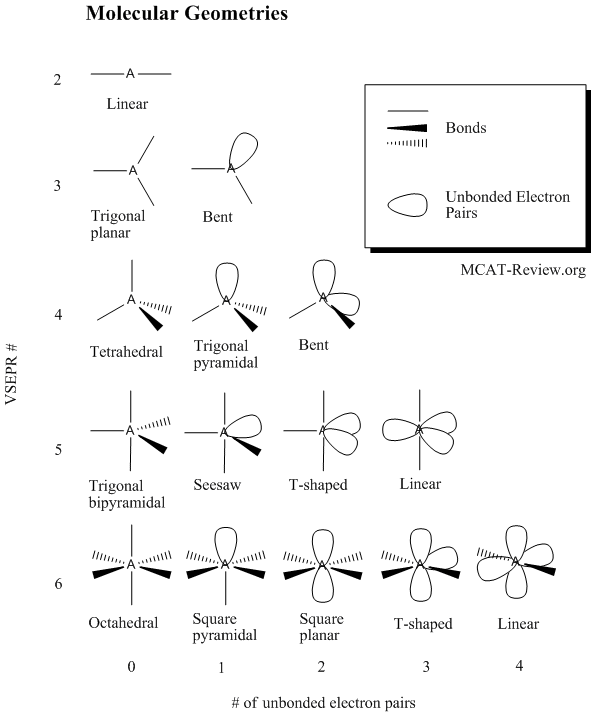
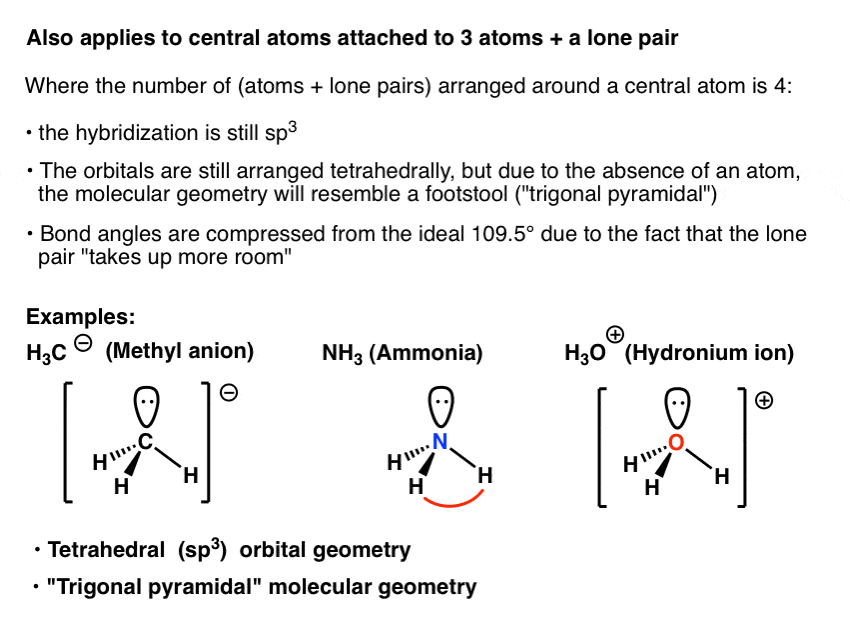
Molecular bond angles chart. The bond dipoles are colored magenta and the resulting molecular dipole is colored blue. Its bond angles are 90 and 120 where the equatorial equatorial bonds are 120 apart from one another and all other angles are 90. For bent molecular geometry when the electron pair geometry is tetrahedral the bond angle is around 105 degrees.
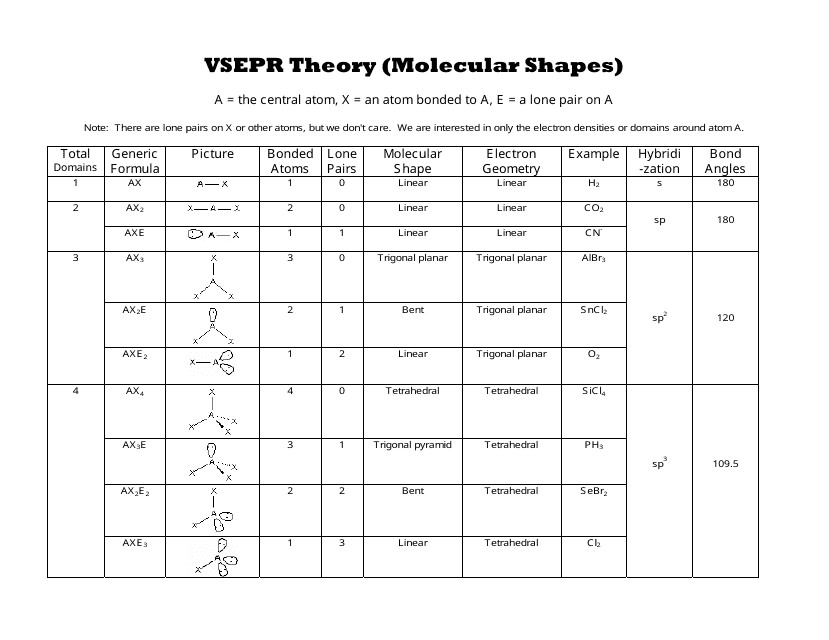
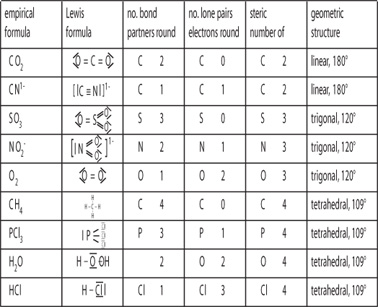
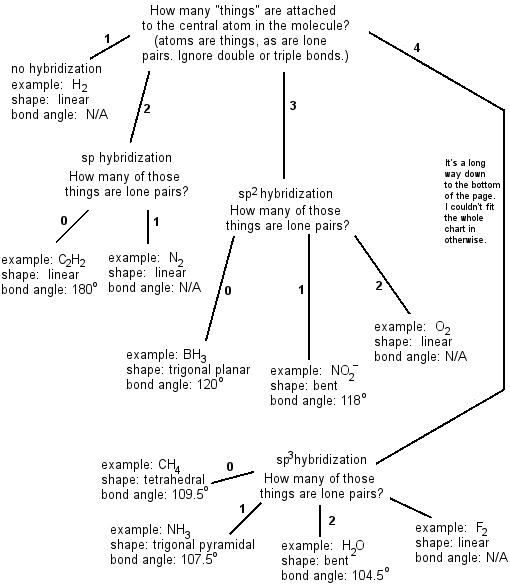
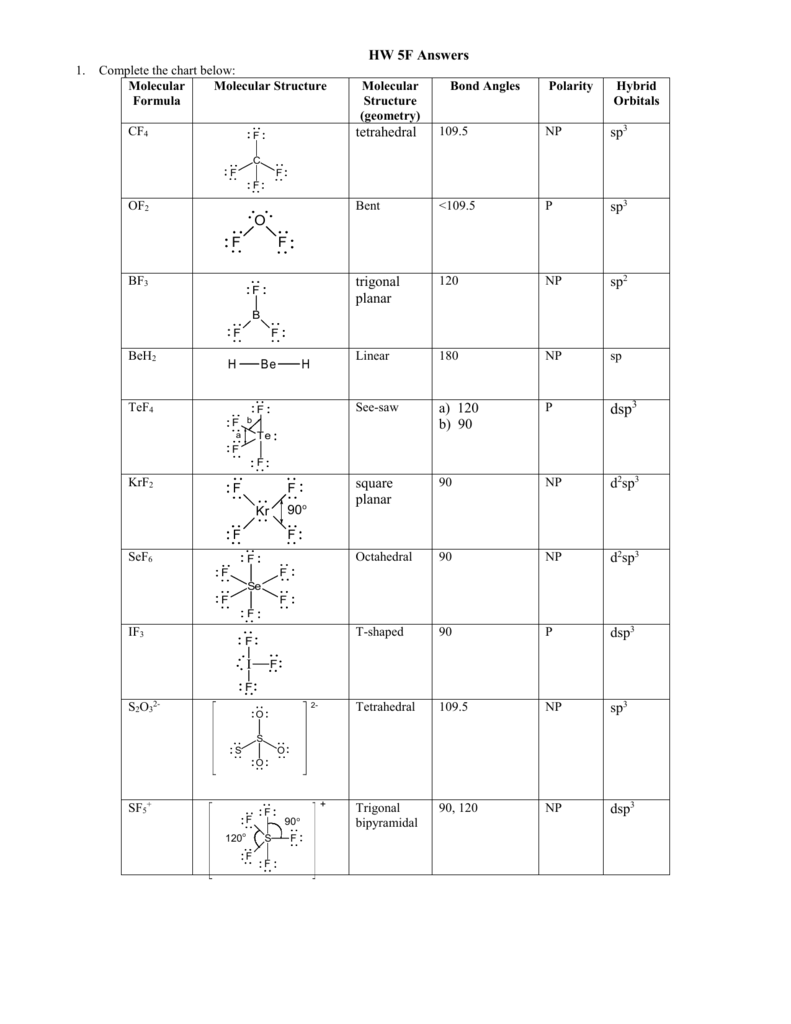
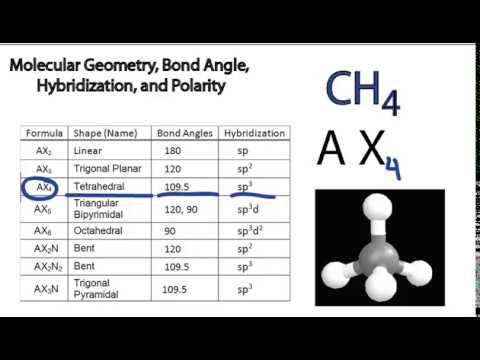
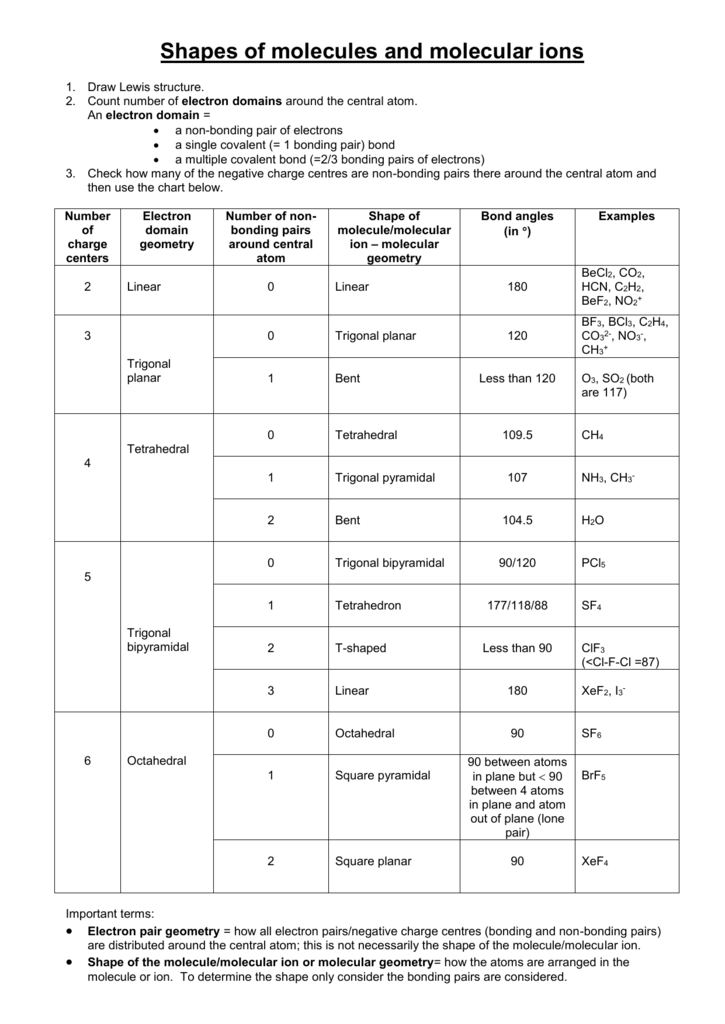
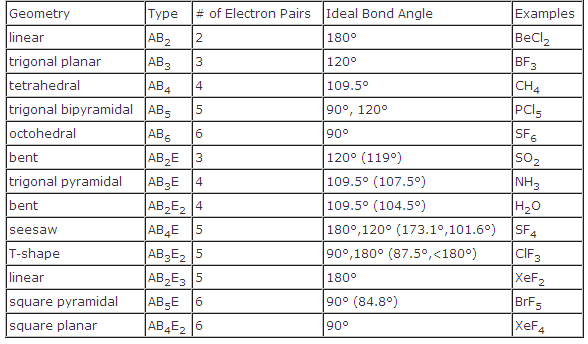
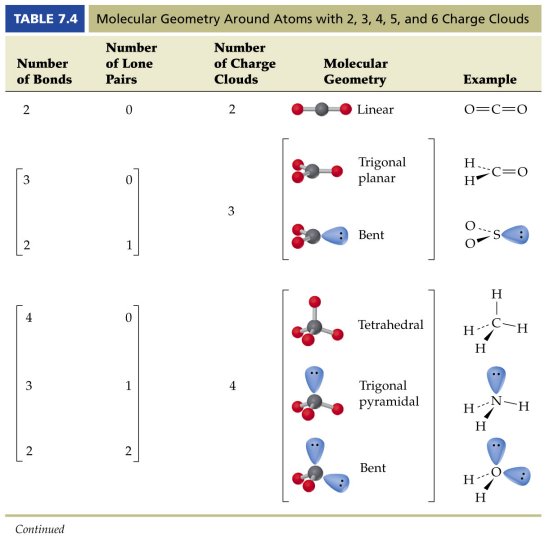
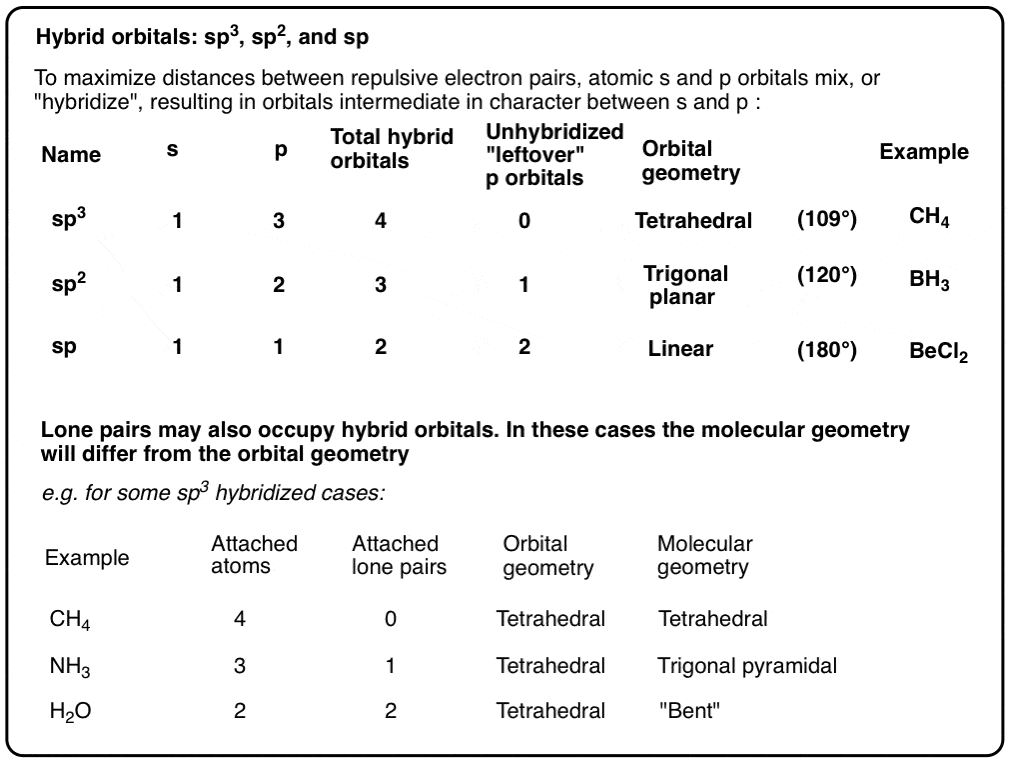
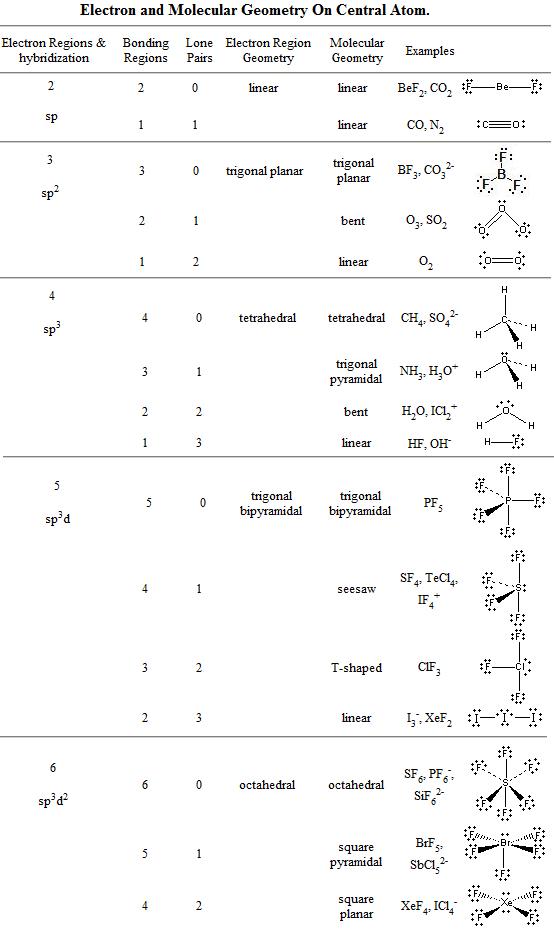
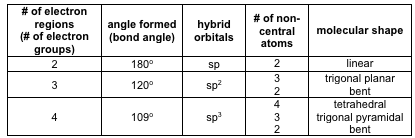
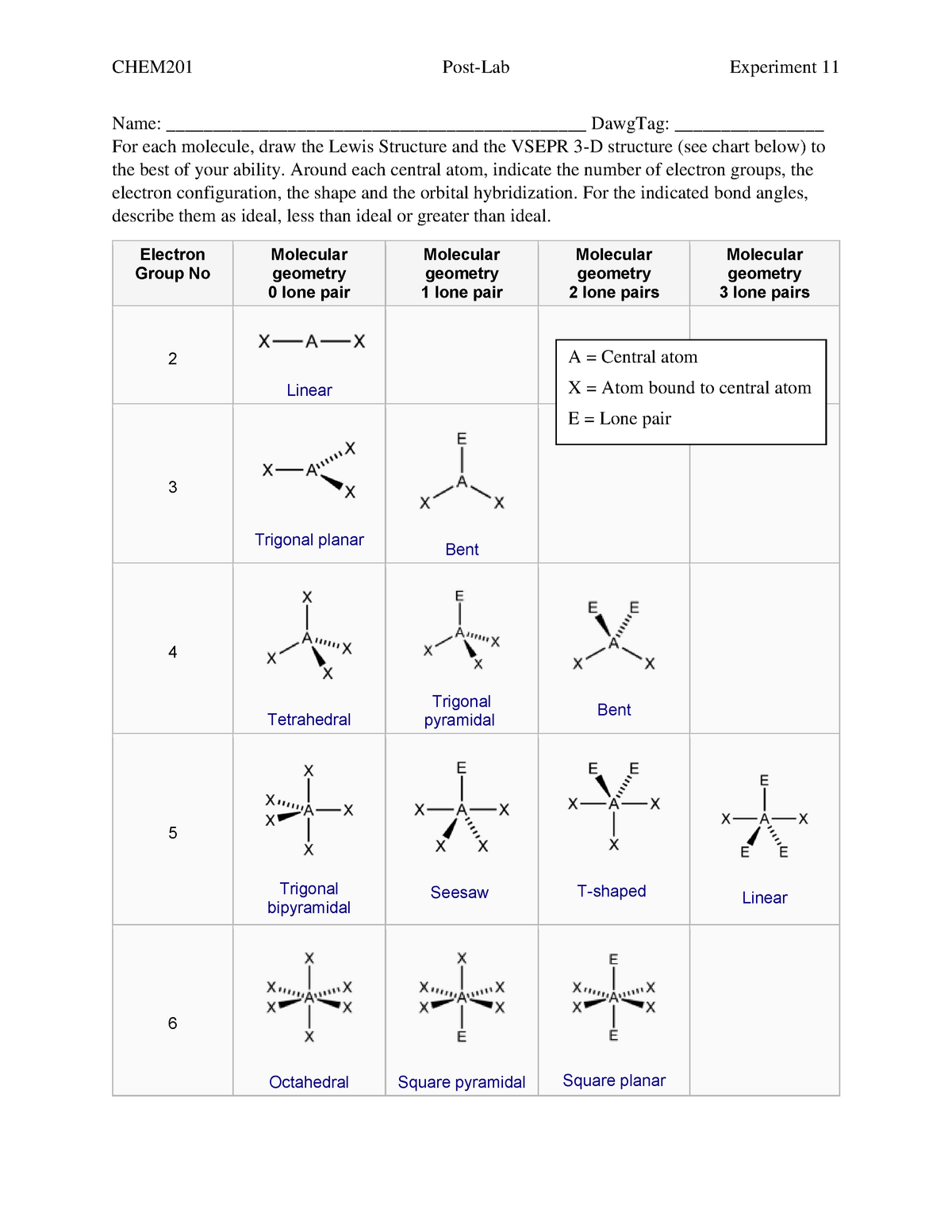
3 molecular shape bond angles polarity hybrid ization appearance 2 linear 2 0 ax 2 linear 180 nonpolar 4 sp 180 3 5 trigonal planar 3 0 ax 3 trigonal planar 120 nonpolar4 sp2 120 2 1 ax 2e bent 120 polar sp 2 120 4 tetrahedral 4 0 ax 4 tetrahedral 109 5 nonpolar 4 sp3 109 5 3 1 ax 3e trigonal pyramidal 109 5 polar sp3 109. Molecular geometry influences several properties of a substance including its reactivity polarity phase of matter color magnetism and biological activity. We can draw the lewis structure on a sheet of paper.
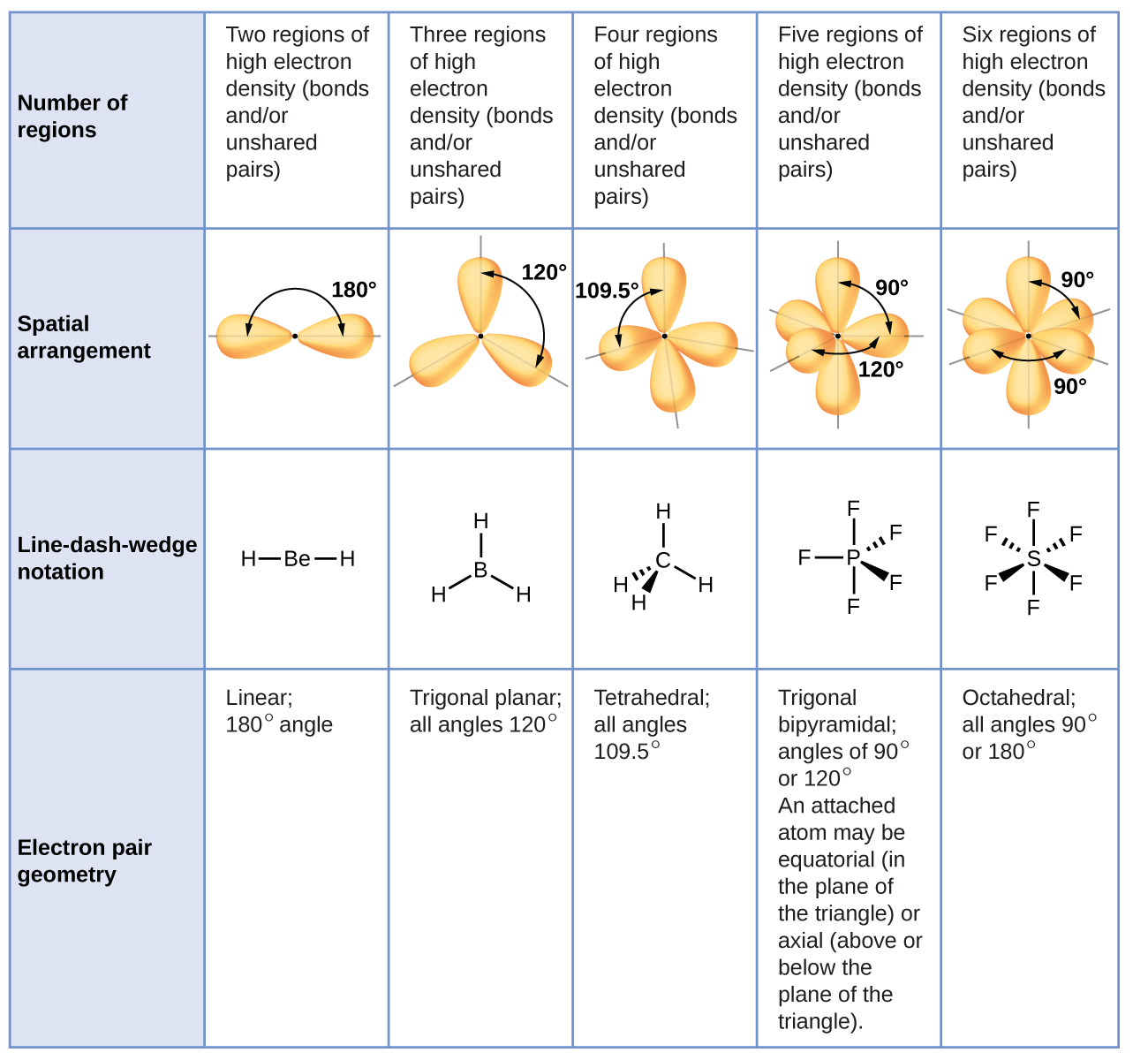
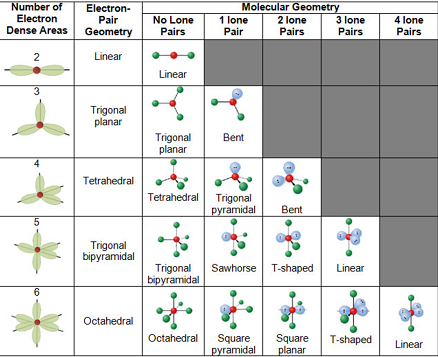
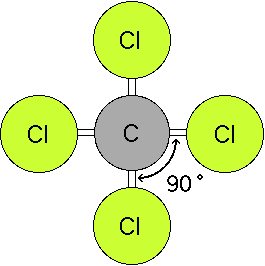
Molecular geometry describes the three dimensional arrangement of atoms in a molecule. Total of electrons. The bond angles are all 90 and just as four electron pairs experience minimum repulsion when they are directed toward the corners of a tetrahedron six electron pairs try to point toward the corners of an octahedron.
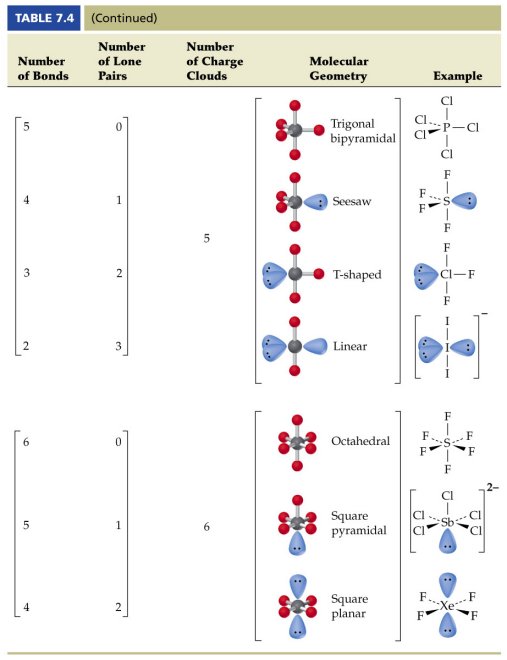
For trigonal pyramidal geometry the bond angle is slightly less than 109 5 degrees around 107 degrees. Data that may be obtained from a molecule s geometry includes the relative position of each atom bond lengths bond angles and torsional angles. An example of an octahedral molecule ax 6 is sulfur hexafluoride sf 6.
Now choose so 2 in so 2 total three electron density areas but two of them are bonding and one is lone pair. Choose bf3 molecule under real molecule section and click on the molecular geometry electronic geometry and bond angle. For other bond angles 120 to 90º the molecular dipole would vary in size being largest for the 90º configuration.
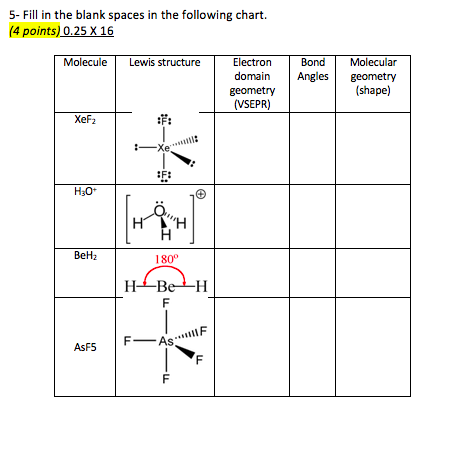
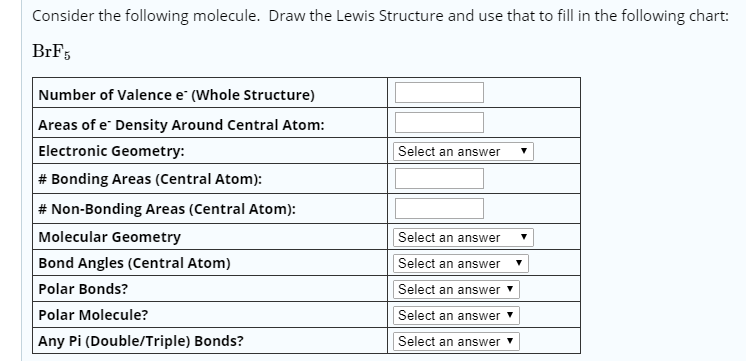
Molecular geometry is the three dimensional arrangement of the atoms that constitute a molecule. Lets consider the lewis structure for ccl 4. Molecular shape electron geometry example hybridi zation bond angles ax 5 5 0 trigonal bipyramid trigonal bipyramid asf 5 ax 4e 4 1 see saw trigonal bipyramid seh 4 ax 3e 2 3 2 t shape trigonal bipyramid icl 3 5 ax 2e 3 2 3 linear trigonal bipyramid brf 2 sp3d 90 and 120 ax 6 6 0 octahedral octahedral secl 6 ax 5e 5 1 square pyramid octahedral.
90 120 polar has a dipole moment. It includes the general shape of the molecule as well as bond lengths bond angles torsional angles and any other geometrical parameters that determine the position of each atom.